4 min read
Preparations for Next Moonwalk Simulations Underway (and Underwater)
NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, is preparing today for tomorrow’s mission. Supersonic flight, next generation aircraft, advanced air mobility, climate changes, human exploration of space, and the next innovation are just some of the topics our researchers, engineers, and mission support teams focused on in 2024.
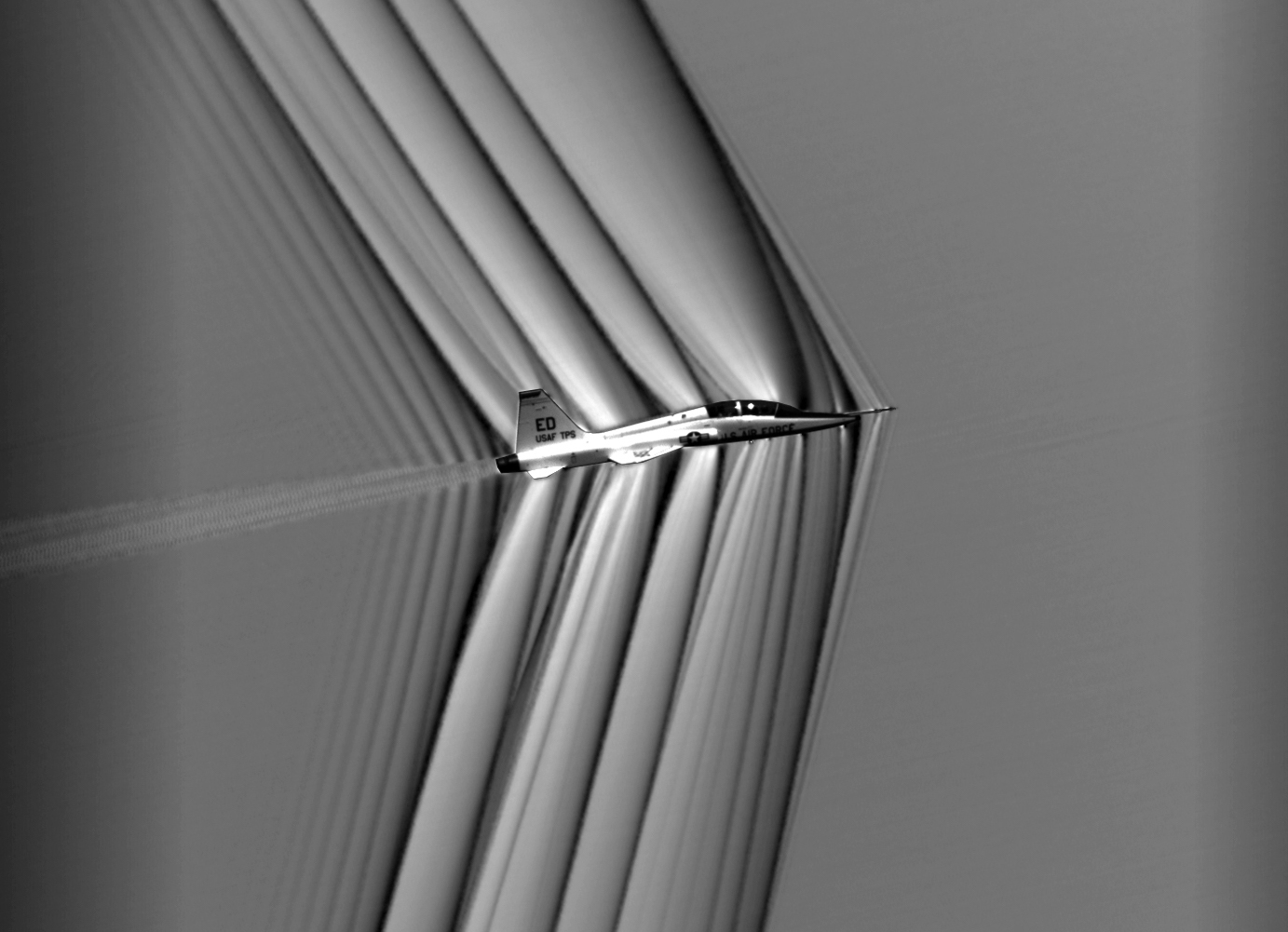
NASA Armstrong began 2024 with the public debut of the X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft. Through the unique design of the X-59, NASA aims to reduce the sonic boom to make it much quieter, potentially opening the future to commercial supersonic flight over land. Throughout the first part of the year, NASA and international researchers studied air quality across Asia as part of a global effort to better understand the air we breathe. Later in the year, for the first time, a NASA-funded researcher conducted an experiment aboard a commercial suborbital rocket, studying how changes in gravity during spaceflight affect plant biology.
Here’s a look at more NASA Armstrong accomplishments throughout 2024:
- Our simulation team began work on NASA’s X-66 simulator, which will use an MD-90 cockpit and allow pilots and engineers to run real-life scenarios in a safe environment.
- NASA Armstrong engineers completed and tested a model of a truss-braced wing design, laying the groundwork for improved commercial aircraft aerodynamics.
- NASA’s Advanced Air Mobility mission and supporting projects worked with industry partners who are building innovative new aircraft like electric air taxis. We explored how these new designs may help passengers and cargo move between and inside cities efficiently. The team began testing with a custom virtual reality flight simulator to explore the air taxi ride experience. This will help designers create new aircraft with passenger comfort in mind. Researchers also tested a new technology that will help self-flying aircraft avoid hazards.
- A NASA-developed computer software tool called OVERFLOW helped several air taxi companies predict aircraft noise and aerodynamic performance. This tool allows manufacturers to see how new design elements would perform, saving the aerospace industry time and money.
- Our engineers designed a camera pod with sensors at NASA Armstrong to help advance computer vision for autonomous aviation and flew this pod at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
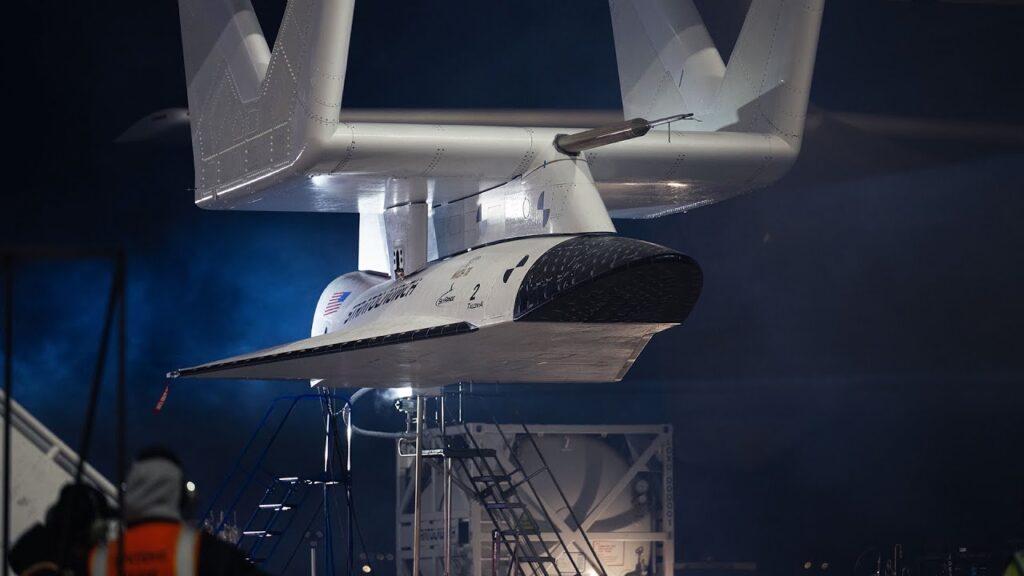
- NASA’s Quesst mission marked a major milestone with the start of tests on the engine that will power the quiet supersonic X-59 experimental aircraft.
- In February and March, NASA joined international researchers in Asia to investigate pollution sources. The now retired DC-8 and NASA Langley Gulfstream III aircraft collected air measurements over the Philippines, South Korea, Malaysia, Thailand, and Taiwan. Combined with ground and satellite observations, these measurements continue to enrich global discussions about pollution origins and solutions.
- The Gulfstream IV joined NASA Armstrong’s fleet of airborne science platforms. Our teams modified the aircraft to accommodate a next-generation science instrument that will collect terrain information of the Earth in a more capable, versatile, and maintainable way.
- The ER-2 and the King Air supported the development of spaceborne instruments by testing them in suborbital settings. On the Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem Postlaunch Airborne eXperiment mission (PACE-PAX), the ER-2 validated data collected by the PACE satellite about the ocean, atmosphere, and surfaces.
- Operating over several countries, researchers onboard NASA’s C-20A collected data and images of Earth’s surface to understand global ecosystems, natural hazards, and land surface changes. Following Hurricane Milton, the C-20A flew over affected areas to collect data that could help inform disaster response in the future.
- We also tested nighttime precision landing technologies that safely deliver spacecraft to hazardous locations with limited visibility.
- With the goal to improve firefighter safety, NASA, the U.S. Forest Service, and industry tested a cell tower in the sky. The system successfully provided persistent cell coverage, enabling real-time communication between firefighters and command posts.
- Using a 1960s concept wingless, powered aircraft design, we built and tested an atmospheric probe to better and more economically explore giant planets.
- NASA Armstrong hosted its first Ideas to Flight workshop, where subject matter experts shared how to accelerate research ideas and technology development through flight.
These are just some of NASA Armstrong’s many innovative research efforts that support NASA’s mission to explore the secrets of the universe for the benefit of all.